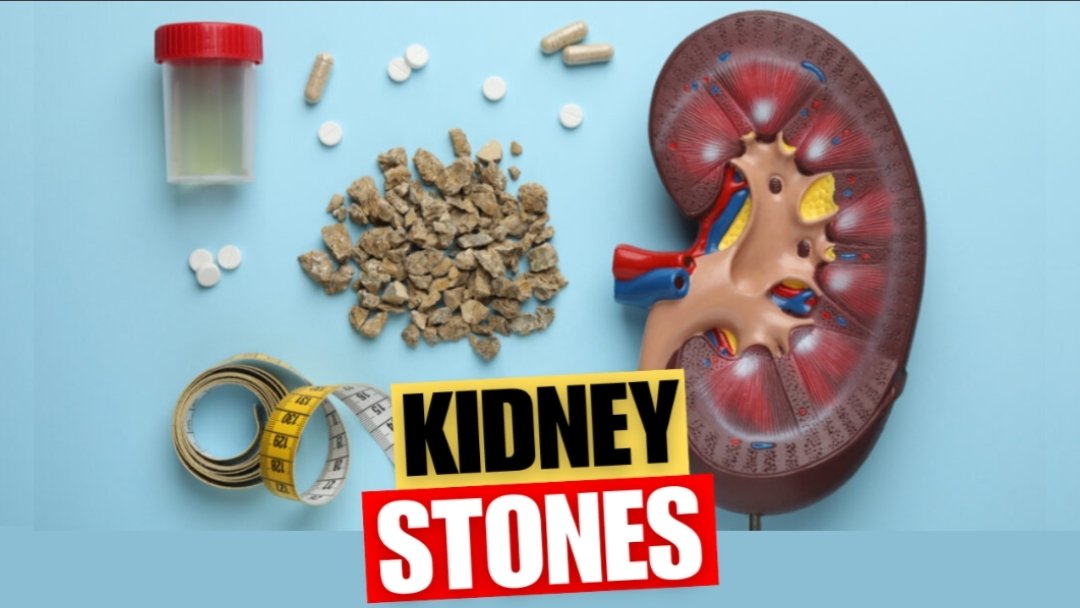
Kidney stones are a common and often painful condition that occurs when minerals and salts in urine crystallize and form solid masses within the kidneys or urinary tract.
While kidney stone vary in size and composition, they can cause significant discomfort and may require medical intervention to manage effectively.
Table of Contents
What Causes Kidney Stones?
Several factors contribute to the formation of kidney stone, including:
1. Dehydration: Insufficient fluid intake can lead to concentrated urine, increasing the risk of stone formation.
2. Dietary Factors: Consuming foods high in oxalate, such as spinach, nuts, and chocolate, or high in salt and protein, can contribute to stone formation.
3. Genetics: A family history of kidney stone can increase an individual’s susceptibility to developing them.
4. Certain Medical Conditions: Conditions such as hyperparathyroidism, cystic kidney diseases, and urinary tract infections can predispose individuals to kidney stone formation.
5. Medications: Some medications, including diuretics and antacids containing calcium, can increase the risk of developing kidney stone.
Sii Daalaco: Youtubekeyga
Symptoms of Kidney Stones
The symptoms of kidney stone can vary depending on the size and location of the stone within the urinary tract. Common symptoms include:
1. Severe Pain: The most characteristic symptom of kidney stone is intense pain, typically felt in the back or side, often radiating to the lower abdomen or groin. The pain may come in waves and fluctuate in intensity.
2. Blood in Urine: Hematuria, or the presence of blood in the urine, can occur due to irritation of the urinary tract by the stone.
3. Urinary Symptoms: Individuals with kidney stone may experience frequent urination, urgency to urinate, or pain or burning during urination.
4. Nausea and Vomiting: Some people with kidney stones may experience nausea, vomiting, or abdominal discomfort.
Diagnosing and Treating Kidney Stones
If you suspect you have kidney stones, it’s essential to seek medical evaluation for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Diagnosis may involve:
1. Medical History and Physical Examination: Your healthcare provider will inquire about your symptoms and medical history and conduct a physical examination.
2. Imaging Tests: Imaging studies such as a CT scan, ultrasound, or X-ray may be performed to visualize the stones and assess their size and location.
3. Urinalysis: Analysis of a urine sample can help identify any underlying conditions contributing to stone formation.
Treatment options for kidney stones depend on factors such as the size and location of the stones, as well as the severity of symptoms.
Common treatment approaches include:
1. Pain Management: Over-the-counter or prescription pain medications may be prescribed to alleviate discomfort associated with kidney stones.
2. Hydration: Drinking plenty of water can help flush out small stones and prevent the formation of new ones.
3. Medication: Certain medications, such as alpha-blockers or medications to control urinary acid levels, may be prescribed to help facilitate the passage of stones.
4. Medical Procedures: In cases where stones are large or causing severe symptoms, medical procedures such as shock wave lithotripsy, ureteroscopy, or surgical removal may be necessary.
Preventing Kidney Stones
While not all kidney stones can be prevented, several lifestyle modifications can help reduce the risk of stone formation:
1. Stay Hydrated: Drinking an adequate amount of water each day helps dilute urine and prevent the formation of concentrated crystals.
2. Dietary Modifications: Limiting intake of foods high in oxalate, sodium, and animal protein can help reduce the risk of stone formation.
3. Calcium Intake: Consuming calcium-rich foods or taking calcium supplements with meals can help bind oxalate in the intestines, reducing its absorption and excretion in the urine.
4. Monitor Sodium Intake: Excessive sodium intake can increase calcium excretion in the urine, contributing to stone formation. Limiting sodium intake can help prevent this.
5. Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can help maintain a healthy weight and reduce the risk of developing certain medical conditions associated with kidney stones, such as obesity and high blood pressure.
Sii Daalaco: Facebook pagekeyga
Conclusion
Kidney stones can cause significant pain and discomfort, but with proper diagnosis and treatment, most stones can be effectively managed or passed without complications.
By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for kidney stones, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce their risk and promote overall urinary tract health.
If you suspect you have kidney stones or experience symptoms suggestive of their presence, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider for proper evaluation and management.
Look about this: Kidney Infections



Pingback: The Liver: Anatomy And Physiology 2024